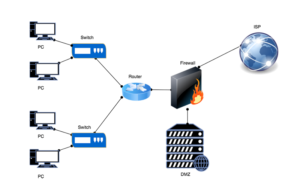
Firewalls
A firewall is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It establishes a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet.
Types of Firewalls:
- Packet-Filtering Firewalls:
- Function: Inspect packets and block them if they don’t meet predefined security rules.
- Pros: Simple and effective for basic traffic control.
- Cons: Limited protection; can’t inspect packet payloads.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls:
- Function: Monitor the state of active connections and make decisions based on the context of traffic.
- Pros: More secure than packet-filtering; tracks state of connections.
- Cons: Can be resource-intensive.
- Proxy Firewalls:
- Function: Intermediary between users and the internet, filtering traffic at the application level.
- Pros: High level of security; can inspect entire messages.
- Cons: Can slow down network performance.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW):
- Function: Include traditional firewall functions along with advanced features like application awareness, integrated intrusion prevention, and cloud-delivered threat intelligence.
- Pros: Comprehensive security; deep packet inspection.
- Cons: More complex and expensive.





 AMC / Tech Service
AMC / Tech Service IT Infrastructure
IT Infrastructure Telecommunication
Telecommunication Surveillance CCTV
Surveillance CCTV Access Control
Access Control Web & Marketing
Web & Marketing